大型会展参观者人流仿真研究
摘要近年来随着会展行业的发展,参观者人流行动规律的研究正逐渐开始显现其必要性。尤其是2010年世博会将在上海举行,届时预计将有七千万人次前来参观,每日五十万左右人次的人流量将是对整个世博会管理的严峻考验,同时也对整个国内的会展的管理行业提出了新的要求。本文主要选取2008年9月9日至11月16日在上海美术馆举办的双年展作为研究对象,从研究诸如双年展这种日参观量五千人左右的规模的会展着手,结合实际的场馆类型总结出一套行之有效的参观者人流的分析方法,并利用基于引力模型的效用函数对参观行为进行改进,接着用软件将人流的行为进行仿真。通过对仿真结果的分析可得出场馆内各个展点的人流拥挤情况,参观者的参观耗...
相关推荐
-
5 二年级语文上册期末教学质量检测试卷(含答案)部编版VIP免费
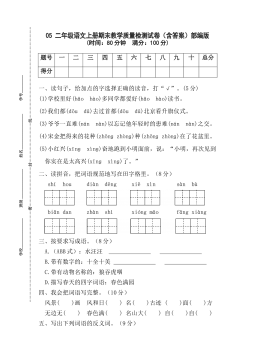
 2024-11-19 12
2024-11-19 12 -
4 二年级语文上册期末教学质量检测试卷(含答案)部编版VIP免费

 2024-11-19 41
2024-11-19 41 -
3 二年级语文上册期末教学质量检测试卷(含答案)部编版VIP免费
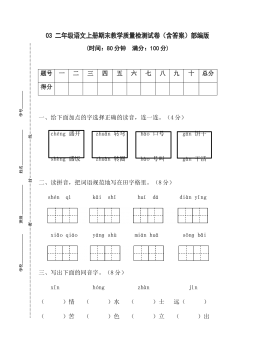
 2024-11-19 20
2024-11-19 20 -
2 二年级语文上册期末教学质量检测试卷(含答案)部编版VIP免费
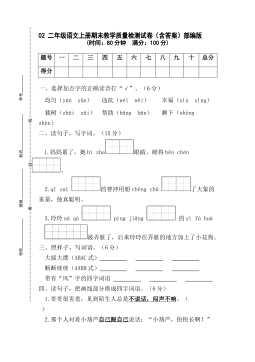
 2024-11-19 29
2024-11-19 29 -
1二年级语文上册期末教学质量检测试卷(含答案)部编版VIP免费
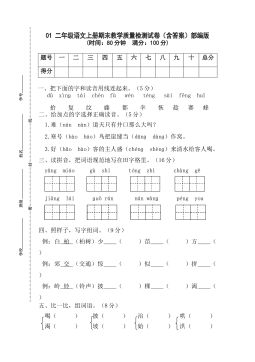
 2024-11-19 16
2024-11-19 16 -
【满分冲刺】2021-2022学年二年级语文上册期末考试尖子生突破卷 部编版(含答案)VIP免费
 2024-11-19 75
2024-11-19 75 -
【精品】二年级上册语文试题-期中考试模拟卷-部编版(含答案)VIP免费

 2024-11-19 80
2024-11-19 80 -
【冲刺百分】二年语文上册期末冲刺模拟试卷(B) (有答案)VIP免费
 2024-11-19 23
2024-11-19 23 -
【冲刺百分】二年语文上册期末冲刺模拟试卷(A) (有答案)VIP免费
 2024-11-19 16
2024-11-19 16 -
第六单元试题(B)二年级上册语文(部编含答案)VIP免费
 2024-11-19 20
2024-11-19 20
相关内容
-

【满分冲刺】2021-2022学年二年级语文上册期末考试尖子生突破卷 部编版(含答案)
分类:中小学教育资料
时间:2024-11-19
标签:无
格式:DOC
价格:5 积分
-

【精品】二年级上册语文试题-期中考试模拟卷-部编版(含答案)
分类:中小学教育资料
时间:2024-11-19
标签:无
格式:DOC
价格:5 积分
-

【冲刺百分】二年语文上册期末冲刺模拟试卷(B) (有答案)
分类:中小学教育资料
时间:2024-11-19
标签:无
格式:DOCX
价格:5 积分
-

【冲刺百分】二年语文上册期末冲刺模拟试卷(A) (有答案)
分类:中小学教育资料
时间:2024-11-19
标签:无
格式:DOCX
价格:5 积分
-

第六单元试题(B)二年级上册语文(部编含答案)
分类:中小学教育资料
时间:2024-11-19
标签:无
格式:DOC
价格:5 积分






