Ad hoc网络无载波感知的功率控制MAC协议的研究及退避算法的改进
目录中文摘要ABSTRACT第一章绪论........................................................1§1.1Adhoc网络概论...........................................1§1.1.1Adhoc网络简介......................................1§1.1.2Adhoc网络的特点....................................2§1.1.3Adhoc网络的应用....................................4§1.1.4A...
相关推荐
-
5 二年级语文上册期末教学质量检测试卷(含答案)部编版VIP免费
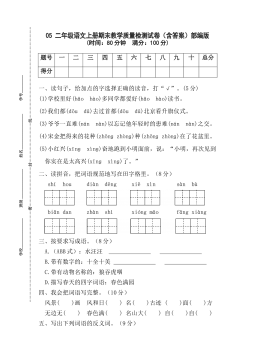
 2024-11-19 12
2024-11-19 12 -
4 二年级语文上册期末教学质量检测试卷(含答案)部编版VIP免费

 2024-11-19 41
2024-11-19 41 -
3 二年级语文上册期末教学质量检测试卷(含答案)部编版VIP免费
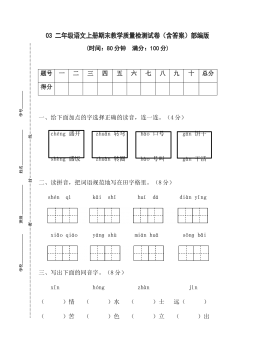
 2024-11-19 20
2024-11-19 20 -
2 二年级语文上册期末教学质量检测试卷(含答案)部编版VIP免费
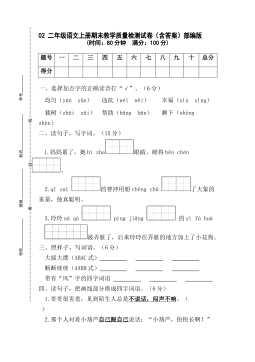
 2024-11-19 29
2024-11-19 29 -
1二年级语文上册期末教学质量检测试卷(含答案)部编版VIP免费
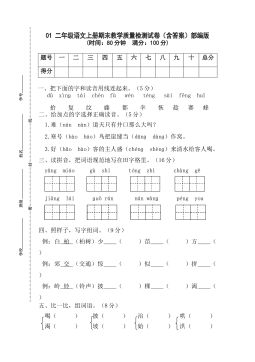
 2024-11-19 16
2024-11-19 16 -
【满分冲刺】2021-2022学年二年级语文上册期末考试尖子生突破卷 部编版(含答案)VIP免费
 2024-11-19 75
2024-11-19 75 -
【精品】二年级上册语文试题-期中考试模拟卷-部编版(含答案)VIP免费

 2024-11-19 80
2024-11-19 80 -
【冲刺百分】二年语文上册期末冲刺模拟试卷(B) (有答案)VIP免费
 2024-11-19 23
2024-11-19 23 -
【冲刺百分】二年语文上册期末冲刺模拟试卷(A) (有答案)VIP免费
 2024-11-19 16
2024-11-19 16 -
第六单元试题(B)二年级上册语文(部编含答案)VIP免费
 2024-11-19 20
2024-11-19 20
相关内容
-

【满分冲刺】2021-2022学年二年级语文上册期末考试尖子生突破卷 部编版(含答案)
分类:中小学教育资料
时间:2024-11-19
标签:无
格式:DOC
价格:5 积分
-

【精品】二年级上册语文试题-期中考试模拟卷-部编版(含答案)
分类:中小学教育资料
时间:2024-11-19
标签:无
格式:DOC
价格:5 积分
-

【冲刺百分】二年语文上册期末冲刺模拟试卷(B) (有答案)
分类:中小学教育资料
时间:2024-11-19
标签:无
格式:DOCX
价格:5 积分
-

【冲刺百分】二年语文上册期末冲刺模拟试卷(A) (有答案)
分类:中小学教育资料
时间:2024-11-19
标签:无
格式:DOCX
价格:5 积分
-

第六单元试题(B)二年级上册语文(部编含答案)
分类:中小学教育资料
时间:2024-11-19
标签:无
格式:DOC
价格:5 积分






